Introduction
In today’s energy-conscious world, the light shines on the concept of light efficiency more brightly than ever. As we navigate through the challenges of environmental sustainability and energy conservation, the role of efficient lighting transcends mere functionality—it becomes a key player in the global effort to reduce energy consumption and carbon footprints. Amidst this backdrop, understanding and optimizing light efficiency is not just beneficial; it’s imperative.
Central to the discourse on light efficiency is the concept of luminous efficacy. This metric, measured in lumens per watt (lm/W), serves as a gauge for evaluating how well a light source converts electrical energy into visible light. Essentially, it tells us how much bang we’re getting for our energy buck. As such, luminous efficacy becomes a crucial yardstick for comparing different lighting technologies, guiding us towards choices that promise not only to illuminate our spaces but to do so in the most energy-efficient manner possible.
Understanding Light Efficiency
Light efficiency represents a critical aspect of modern lighting technology, focusing on maximizing the amount of useful light generated per unit of power consumed. This efficiency isn’t just about producing more light; it’s about doing so in an environmentally responsible and energy-conserving manner. At the heart of measuring this efficiency is the concept of luminous efficacy, a key metric that quantifies the ratio of light output to energy input, expressed in lumens per watt (lm/W). This measure allows us to assess the performance of light sources in converting electrical energy into visible light, highlighting the advancements in lighting technology that lead to more sustainable energy usage.
The significance of light efficiency extends far beyond the technical realm; it plays a pivotal role in global energy conservation efforts and the pursuit of sustainability. Efficient lighting reduces the demand on power plants, which in turn decreases greenhouse gas emissions and the exploitation of natural resources. In residential and commercial settings, it translates to lower electricity bills and a reduced environmental footprint, making it an integral part of achieving a sustainable future.
The Evolution of Lighting Technologies
The journey of lighting technologies is a testament to human ingenuity, marking our progress from the flickering flames of ancient lamps to the brilliant glow of modern LEDs. This historical voyage has been driven by a continuous quest for greater light efficiency, culminating in innovations that have illuminated our world in ways previously unimaginable.
From Incandescence to Illumination
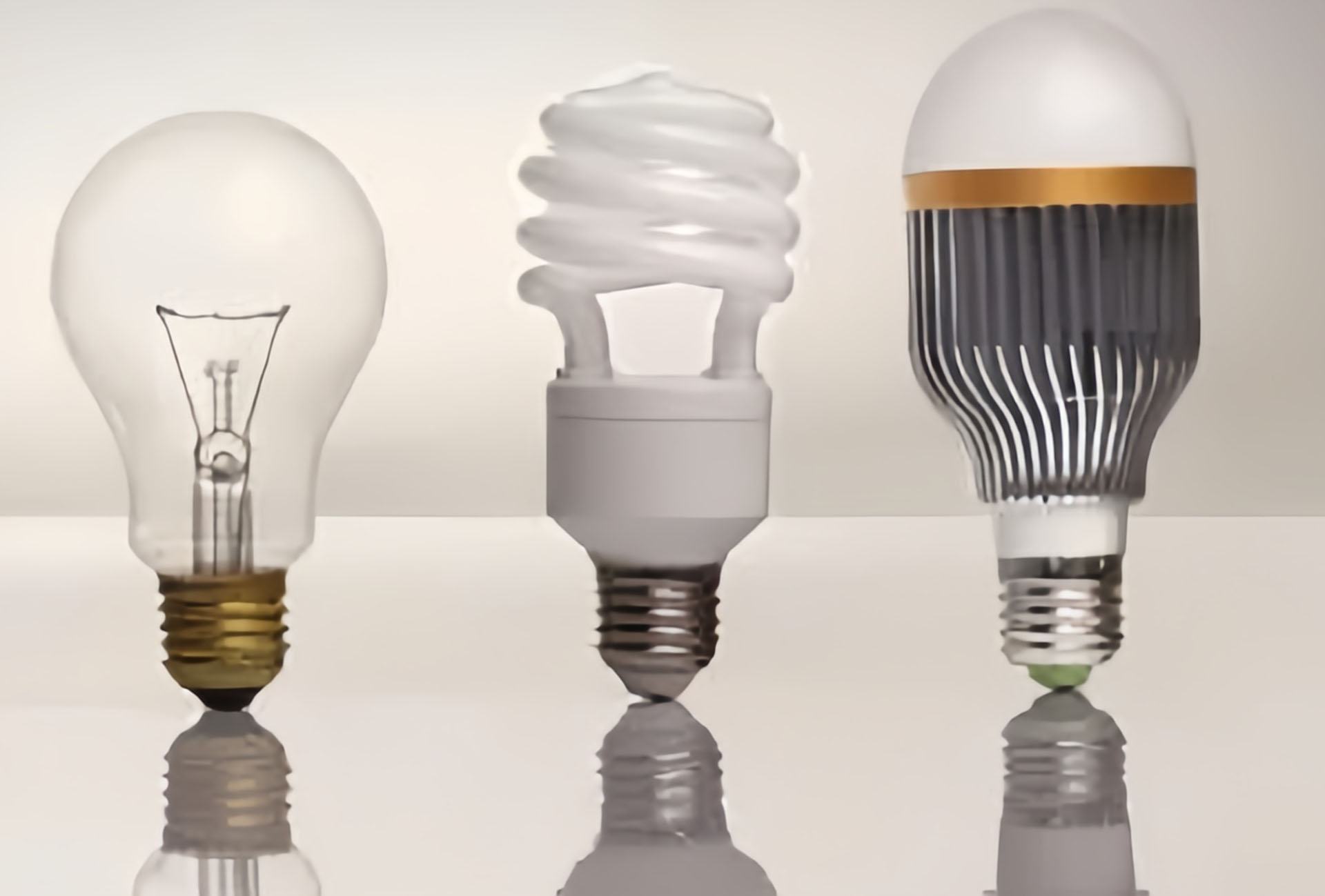
The story begins with the incandescent bulb, patented by Thomas Edison in 1879. These bulbs, producing light through the heating of a filament until it glows, were revolutionary, bringing electric lighting into homes and industries. However, their efficiency was low; most of the energy was lost as heat rather than light. Despite this, incandescent bulbs dominated for over a century due to their simplicity and warm light.
The Fluorescent Leap
The next significant milestone was the development of fluorescent lighting in the early 20th century, commercially introduced in the 1930s. Fluorescent tubes utilized a different mechanism, exciting mercury vapor to emit UV light, which then became visible light when it struck the tube’s phosphor coating. This technology was more energy-efficient than incandescent bulbs and was quickly adopted for commercial and industrial use, offering brighter and more extensive coverage.
Halogen and HID Innovations
Halogen lamps, a refinement of the incandescent bulb, emerged in the 1950s. They offered improved efficiency and longer life by incorporating halogen gas to recycle evaporated tungsten. High-Intensity Discharge (HID) lamps, including metal halide, sodium, and mercury vapor lamps, also gained popularity, especially for outdoor and industrial lighting, thanks to their high luminous efficacy and intense light output.
The LED Revolution
The true revolution in light efficiency began with the advent of Light Emitting Diodes (LEDs). Initially used in the 1960s for indicator lights, LEDs have evolved dramatically. The breakthrough came with the development of blue LEDs in the early 1990s, which, combined with phosphor coatings, allowed for the creation of white light. LEDs are vastly more efficient than previous technologies, converting a higher proportion of electricity into visible light with minimal heat loss. Their long lifespan, durability, and versatility have made LED lighting the cornerstone of modern lighting solutions.

Different lamps efficiency
The Science Behind LED Light Efficiency
LEDs, or Light Emitting Diodes, have revolutionized the concept of light efficiency through their unique working principle and design, setting them apart from traditional lighting technologies. Understanding the science behind LED efficiency illuminates why they have become the preferred choice for sustainable and energy-saving lighting solutions.
How LEDs Work
At the core of an LED is a semiconductor device that emits light when an electric current passes through it. This process, known as electroluminescence, involves electrons moving through the semiconductor material and combining with electron holes, releasing energy in the form of photons, or light. The material and construction of the LED determine the color of the light emitted, with different semiconductors producing different colors.
Why LEDs Are More Efficient
LEDs stand out for their high efficiency for several reasons:
Direct Light Generation: Unlike incandescent bulbs that generate light through heating a filament, or fluorescent lamps that require a gas to be excited, LEDs produce light directly from electricity. This direct conversion results in less energy wasted as heat.
Directional Lighting: LEDs emit light in a specific direction, reducing the need for reflectors and diffusers that can trap light. This directional output ensures that more light reaches the intended area without loss.
Longevity and Durability: LEDs have a longer lifespan compared to traditional bulbs because they are more resistant to switching cycles and lack fragile components like filaments or glass tubes. This durability contributes to their efficiency by reducing the frequency of replacement and maintenance.
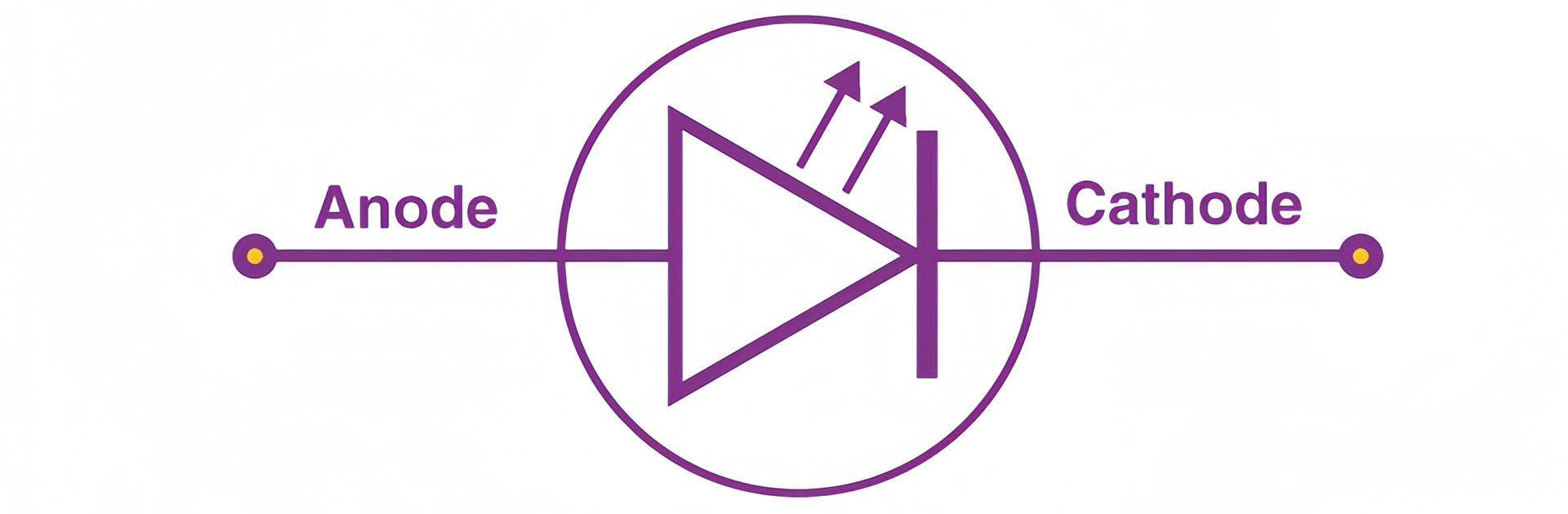
Light-Emitting-Diode
Factors Influencing LED Performance and Longevity
While LEDs are inherently efficient, several factors can affect their performance and longevity:
Thermal Management: Heat is the enemy of LEDs. Although they are cooler than incandescent bulbs, the heat generated within the LED device can degrade the semiconductor material over time if not properly dissipated. Effective thermal management through heat sinks and proper ventilation is crucial to maintaining LED efficiency and lifespan. You can learn more about this reason The Top First Reason For LED Luminaire Failure and Degradation.
Electrical Design: The design of the LED driver, which converts incoming power to the correct voltage and current for the LED, plays a significant role in performance. An improperly designed driver can lead to inefficiencies and shorten the LED’s life.
Quality of Materials: The purity and quality of semiconductor materials used in an LED affect its efficiency and color rendering. High-quality materials ensure that the LED operates at its best performance for longer periods. Learn more about What Factors Affect the Light Efficiency of a LED High Bay Light?
Improving Light Efficiency
The quest for improved light efficiency is a driving force in the lighting industry, with LED technology at the forefront of this pursuit. Innovations in LED efficacy and the integration of materials science are paving the way for the next generation of lighting solutions. Here’s a glimpse into the current research and developments aimed at enhancing LED efficiency and the pivotal role materials science plays in the evolution of future lighting technologies.
Advancements in LED Efficacy
Research in LED technology is relentlessly pushing the boundaries of light efficiency. Scientists and engineers are exploring various avenues to increase the luminous efficacy of LEDs, which measures the amount of light produced per unit of power consumed. Key areas of focus include:
Nanotechnology: By manipulating materials at the nanoscale, researchers are developing LEDs that emit brighter light with less energy input. Nanostructures can alter the way light is emitted and distributed, potentially reducing losses and increasing efficiency.
Phosphor Innovations: The use of new phosphor materials can improve the color rendering of LEDs and enhance efficiency by converting more electrical energy into visible light. Experimenting with different compositions and configurations of phosphor coatings is leading to LEDs with better performance and lower energy consumption.
Quantum Dots: Incorporating quantum dots into LED designs is another area showing promise. Quantum dots can emit light across a broad spectrum of colors with very high efficiency. They offer the potential for tunable lighting solutions that are both energy-efficient and capable of superior color rendering.
The Role of Materials Science in Future Lighting Technologies
Materials science is at the heart of advancements in lighting technology. The development of new materials and the innovative application of existing ones are crucial for the next leaps in light efficiency. Key contributions include:
Semiconductor Materials: Ongoing research into semiconductor materials aims to discover compounds that offer higher efficiency and longer lifespans for LEDs. Innovations in semiconductor technology could lead to LEDs that operate with significantly less power while delivering superior light quality.
Sustainable Materials: As the lighting industry moves towards greener solutions, the exploration of eco-friendly materials for LED production is gaining traction. Researchers are focusing on materials that are not only efficient but also recyclable and less harmful to the environment, aiming to reduce the ecological footprint of lighting products.
Thermal Management Materials: Effective thermal management is vital for maintaining LED efficiency. Advances in materials that dissipate heat more effectively are helping to extend the life of LEDs and enhance their performance. New alloys, ceramics, and composite materials are being developed for use in heat sinks and LED packaging to improve thermal conductivity and heat dispersion.
Improving light efficiency through LED technology and materials science is not just about achieving brighter illumination; it’s about crafting lighting solutions that are sustainable, versatile, and tailored to the needs of the future. As research continues to break new ground, the promise of more efficient, durable, and environmentally friendly lighting becomes increasingly within reach.
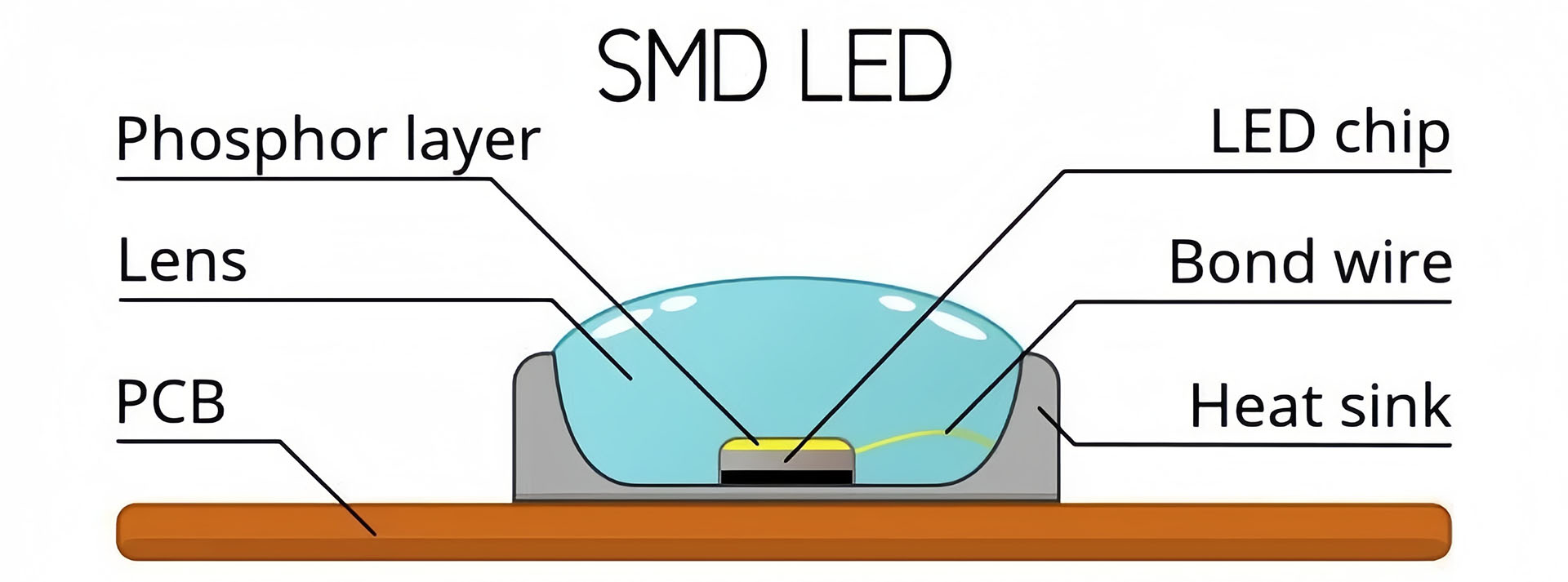
SMD LED Struture
Challenges and Solutions in Maximizing Light Efficiency
While the pursuit of higher light efficiency offers significant benefits, several obstacles can impede progress. Identifying these challenges and implementing strategic solutions is crucial for organizations aiming to enhance their lighting systems’ performance and sustainability.
Common Obstacles to Achieving High Light Efficiency
Upfront Costs: The initial investment required for high-efficiency lighting systems, particularly LEDs, can be a significant barrier for many organizations.
Technological Compatibility: Upgrading to efficient lighting often requires compatibility assessments, as modern LED systems may not integrate seamlessly with existing fixtures or control systems.
Lack of Awareness: A general lack of understanding about the benefits of light efficiency and the options available can hinder adoption.
Thermal Management Issues: Efficiently managing the heat produced by LED lights is critical to ensuring their longevity and performance, posing a technical challenge.
Regulatory and Standardization Gaps: Inconsistent regulations and standards across regions can complicate the adoption of efficient lighting technologies.
Strategies for Overcoming These Challenges
Financing and Incentive Programs: Governments and manufacturers often offer grants, rebates, and financing options to offset the higher initial costs of efficient lighting systems.
Comprehensive Compatibility Assessments: Before upgrading, conducting thorough compatibility assessments can prevent future issues, ensuring that new lighting systems work seamlessly with existing infrastructure.
Educational Initiatives: Providing clear, accessible information about the advantages of light efficiency and the long-term savings it can offer encourages more widespread adoption.
Advanced Thermal Management Solutions: Investing in the latest thermal management technologies, such as improved heat sinks and materials, can solve overheating issues, enhancing LED efficiency and lifespan.
Advocacy for Unified Standards: Engaging in industry advocacy for the development and harmonization of global standards for lighting efficiency can simplify technology adoption and compliance.
By addressing these challenges with targeted strategies, organizations and communities can unlock the full potential of light efficiency. Not only do these solutions pave the way for more widespread adoption of energy-efficient lighting, but they also contribute to broader goals of sustainability and cost reduction. As the lighting industry continues to innovate, overcoming these obstacles becomes a shared endeavor, leading us toward a brighter, more efficient future.

The Future of Light Efficiency
As we stand on the cusp of new advancements in lighting technology, the future of light efficiency appears both promising and transformative. Innovations on the horizon promise to redefine what’s possible, pushing the boundaries of efficiency, sustainability, and functionality. Here’s a glimpse into the emerging technologies and predictions shaping the next frontier in light efficiency.
Emerging Technologies and Innovations
Organic LEDs (OLEDs) and Quantum Dots: OLED technology, with its ability to provide soft, diffused light from extremely thin and flexible panels, is set to revolutionize architectural and design-centric lighting. Quantum dots, with their ability to emit highly saturated colors and efficiency at converting electricity into light, are enhancing LED performance and color rendering.
Li-Fi (Light Fidelity): An innovative technology that uses light waves instead of radio waves to transmit data. While still in developmental stages, Li-Fi could dramatically increase the utility of light fixtures by combining illumination with high-speed data transmission.
Advanced Thermal Management Materials: New materials and designs that more effectively dissipate heat from LEDs will extend their lifespan and improve performance, allowing for more compact and versatile lighting solutions.
Intelligent Lighting Systems: Smart lighting systems that integrate sensors, IoT connectivity, and AI to adapt lighting based on environmental conditions, occupancy, and user preferences are set to become the norm. These systems will enhance energy efficiency while providing personalized lighting experiences.
Conclusion
As we’ve journeyed through the evolving landscape of light efficiency, it’s clear that this pursuit is not just about enhancing illumination but about redefining our relationship with energy and the environment. The importance of light efficiency extends beyond the immediate benefits of reduced energy consumption and lower utility bills. It plays a crucial role in our collective efforts to combat climate change, reduce our ecological footprint, and create sustainable, energy-efficient spaces where we live, work, and play.
The advancements in LED technology, the integration of smart systems, and the exploration of innovative materials have shown us the potential for lighting to transcend its traditional role. Light efficiency now stands as a beacon of progress, symbolizing our ability to harmonize technological advancement with environmental responsibility.
Whether you’re looking to enhance the ambiance of your home, optimize the productivity of your workspace, or brighten public spaces with energy-conscious choices, our expertise is at your disposal. We offer comprehensive guidance on selecting and implementing the most suitable light-efficient technologies for diverse settings.
Reach out to us to start your journey towards smarter, more efficient lighting solutions today. Together, let’s shine a light on sustainability and innovation.
FAQs about Light Efficiency
Get an Instant Quote Now
Let us help you get started with our superior LED lighting products.
Our LED Lighting experts can help to solve your issues.
Before sending your message, please note:
Your message goes to Logos Lighting and it may take time to reply to you.
Please complete all fields unless otherwise indicated. This will help us deal with your inquiry more efficiently. Alternatively, you can contact us directly via email: info@logosled.com.



